

2022-01-09 | 1797 ![]() Print
Print ![]() PDF
PDF
This is a question I have always pondered for a while and I remember I did an awesome post on a similar topic, but a more targetted topic on How to Increase Google Adsense Earnings, you can read on it via the link below (opens a new tab).
Recommended Read: How to Increase Google Adsense Earnings
Since we are going to be talking about traffic I will like us to get familiar with some terminologies below:
AdSense: AdSense is when you place Google Ads on your website, and when a visitor from your website views or clicks on an ad, Google pays you 68% of what the advertiser pays them. It's free to get Adsense to sign up.
CTR: Your ad Click-Through Rate is the number of ad clicks divided by the number of individual ad impressions. Let's assume you are displaying 3 AdSense ads on every page of your website, 1 page view is equal to 3 ad impressions.
CTR = Clicks / Ad Impressions X 100
Suppose, you get 7 clicks out of 3000 ad impressions, your CTR would be 0.23% (7/3000X100).
CPC: Cost Per Click is the revenue you earn each time a visitor clicks on your ad. CPC is determined by the advertisers. In some competitive niches like finance, marketing, online products, etc. advertisers may be willing to pay more per click than others.
CPM: CPM means “Cost Per 1000 Impressions.”
Advertisers can also opt for CPM ads instead of CPC and set their price for 1000 ad impressions. And they pay each time their ads appear on any website.
RPM: Page RPM (“Revenue Per Mille”) is used to calculate the estimated earnings per thousand page views on a website.
Now that you are familiar with the terms, I will like to bring to your attention that this post is not some sort of hack to attain Google's $100 threshold, but rather an exposure as to what is required to get it and even go beyond, don't ever think it is too difficult to meet, we have all started from this platform earning peanuts.
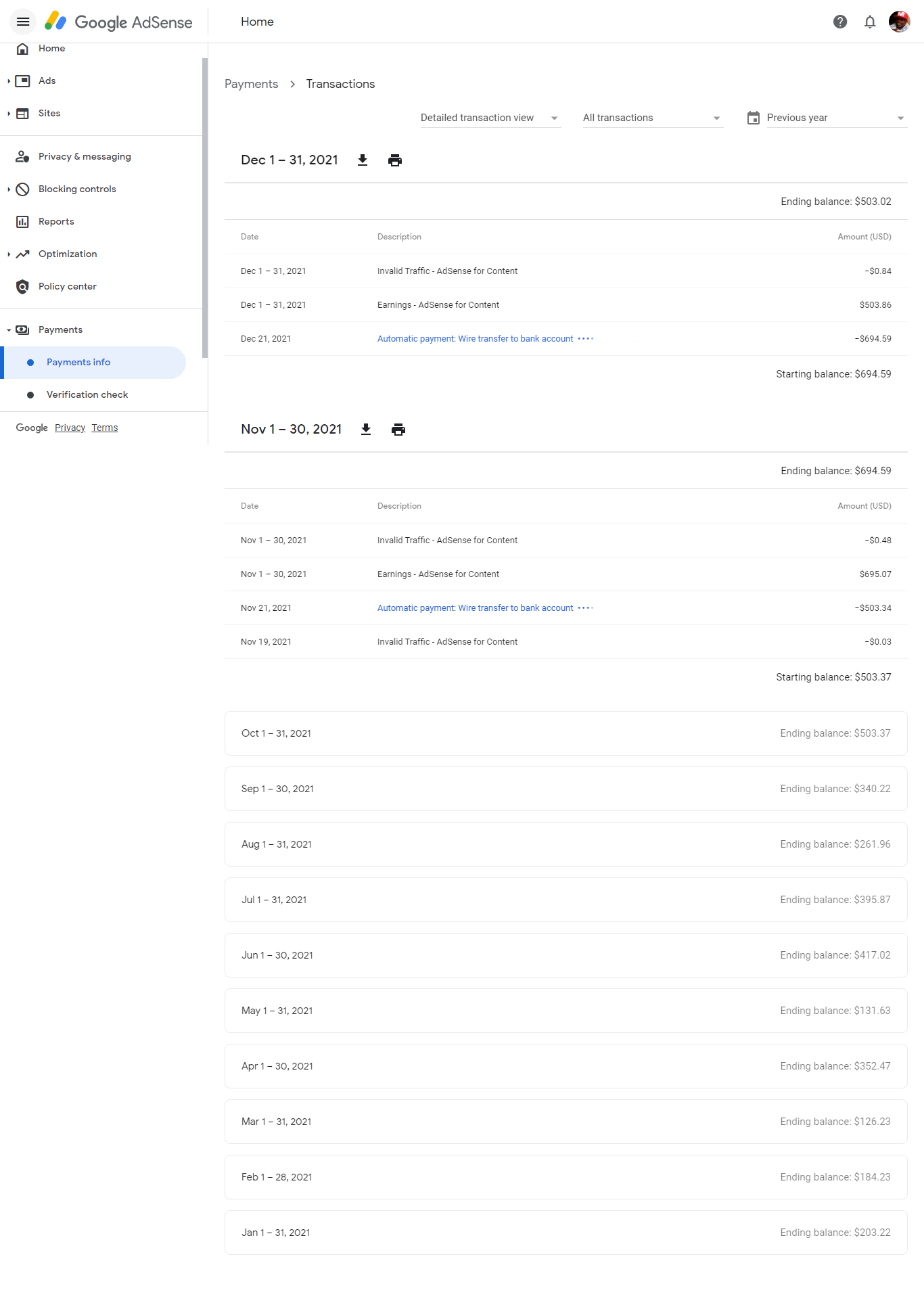
From the diagram illustration above you will notice that we actually started growing our earnings above our average of $200 monthly?
Well, it's from this experiment I was able to deduce the number of traffic required and impressions to earn Google's $100 threshold, if I can do it, so can you.
Please take a closer look at the illustrative diagram below from our Google Adsense earnings dashboard we can deduce that we required 761,000 impressions a 150,000 page views and an RPM of $3.26 (DECREASED BY $2.35) in a duration of 28 days.
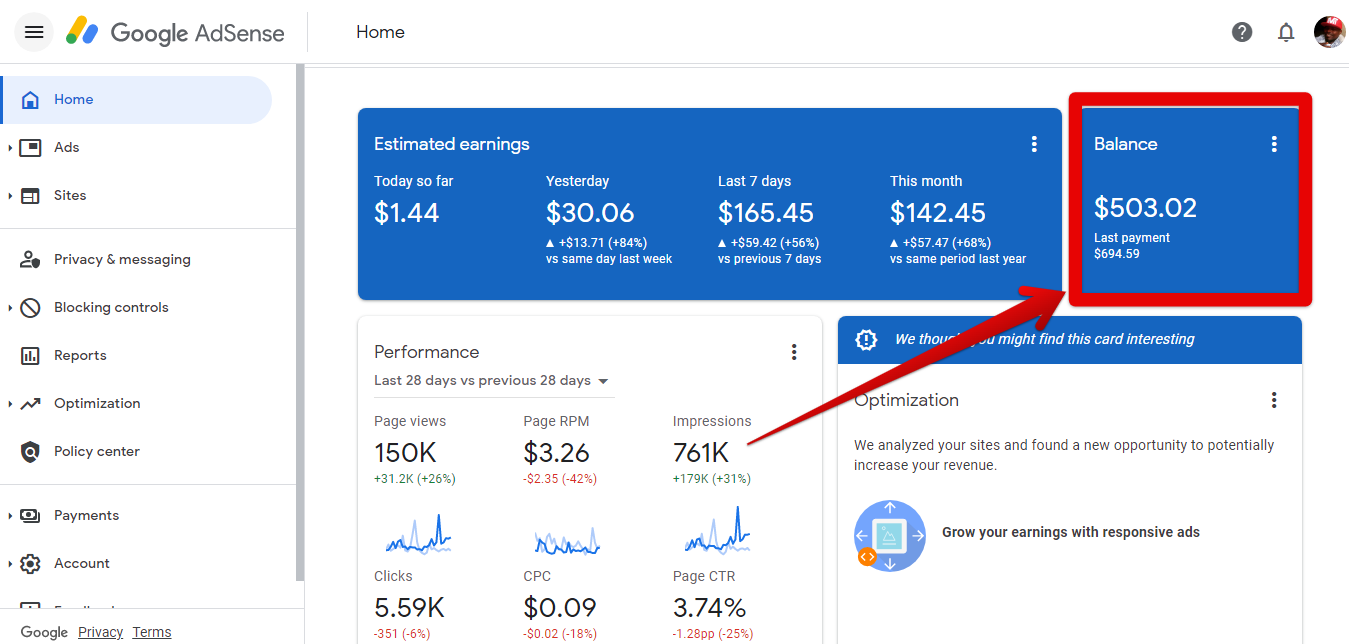
With this information, we can estimate what our earnings can be for instance with the RPM we can calculate an earning from a 10,000 traffic per day
which is WEB TRAFFIC / 1000 x RPM = 36,000/1000 X 3.26 = estimated earning for that day $117.36
So in respect to our headline question, we can understand that two factors are important in earning 100 dollars a day on Google Adsense, one being traffic and the other being RPM.
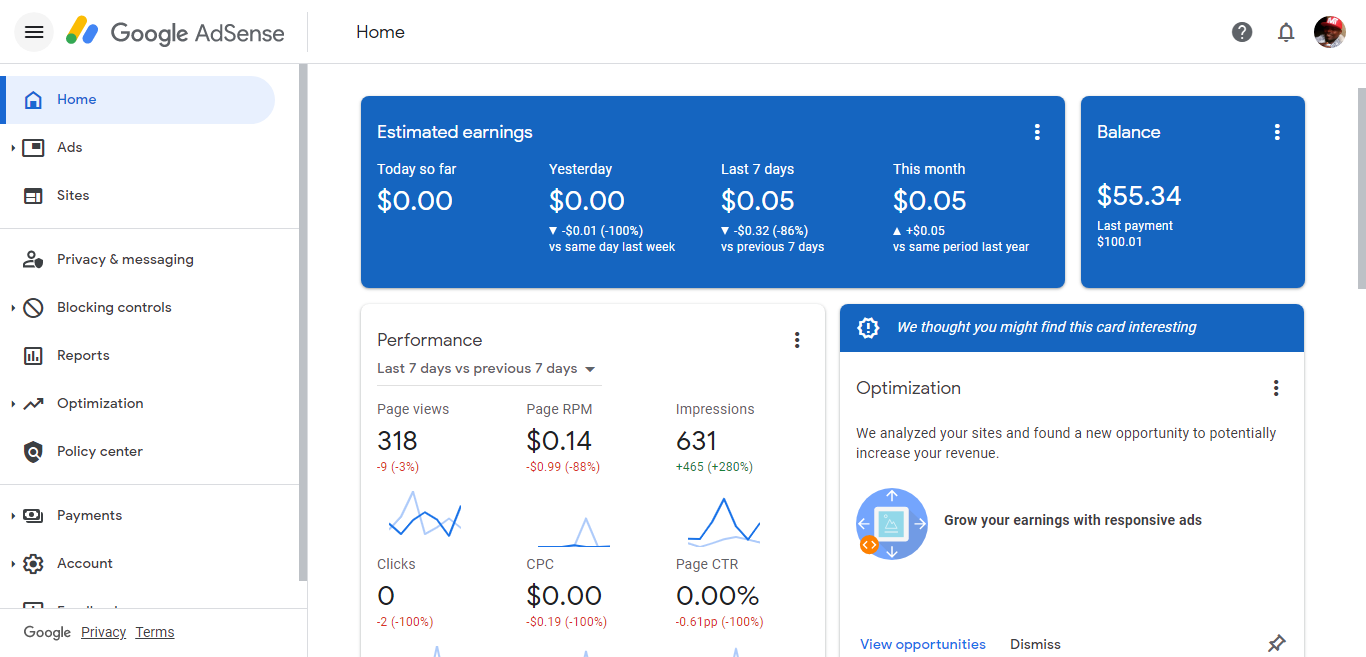
If you have an RPM like the one in this image above then you have a lot of work to do regarding traffic as you will require a massive amount of volume as much as 800,000 a day to hit that 100 dollar benchmark (a day or a month) and improving your RPM, to calculate the RPM value, you need to divide your total estimated earnings by total pageviews during a given time period and multiply by 1000. Another metrics you can look at is the impression RPM you get from the traffic on your pages.
Impression RPM is calculated by dividing your estimated earnings by the number of impressions (ads that have been rendered and displayed), multiplied by 1000.
Impression RPM = (Estimated earnings / Impressions) * 1000
Impression RPM is a metric used to measure how much you will be paid for each impression that is served on your page. It can be a useful metric for running experiments where you need to make like-for-like comparisons, for instance, when you’re running a split test to see which of the two demand partners you’re testing returns better yield for your inventory, which is the purpose of the Google's Adsense Experimental Test.
However, relying only on Impression RPM does not give you the full picture of the revenue pie. For instance, let’s say you decide to drop the least valuable ad units from your inventory, while this might increase Impression RPM, it will decrease your overall revenue.
Since Page RPM simply measures the estimated revenue generated per pageview, one way to increase Page RPM is to increase ad density, i.e., the average number of ad units per page.
However, this is not the best way.
In fact, this is one of the problems with using Page RPM as the primary performance metric—it does not provide any indication of how user experience affects overall revenue.
To optimize Page RPM, you need to either serve more impressions per pageview or increase how much you are paid per impression, ideally both. To increase impressions per page, you can try:
In order to increase the yield per impression, you can try:
Session RPM, also known as EPMV (earnings per thousand visitors), calculates the revenue generated from a thousand visitors/sessions on the website.
Session RPM = (Total earnings / Sessions) * 1000
By connecting revenue directly to visitors, Session RPM allows publishers to fully understand the impact of user experience on revenue. It is therefore a more useful metric compared to Page RPM or other ad unit-level metrics like Impression RPM or Ad Request RPM.
Consider this example: Let’s say a publisher has a Page RPM of $6 and decides to add more ad units on the highest traffic pages. Immediately, the Page RPM shoots up to $8. However, Page RPM does not take into account that because of the negative impact on user experience, the average page views per session drop from 4 to 2. In this case, even though Page RPM increased, the Session RPM decreased from $24 to $16, and overall revenue dropped 33%.
Google AdSense takes record of all these metrics and calculates your earnings within the span of an hour, so if you want to cross-check your inputs on what you have done then you need to do your observation on an hourly duration.

I am a seo web analyst and have a love for anything online marketing. Have been able to perform researches using the built up internet marketing tool; seo web analyst as a case study and will be using the web marketing tool (platform).
How Do You Write Pitch Deck That Wins Investors
Effective Lead Magnet Funnel Examples For Businesses
How To Promote FMCG Products Using Digital Marketing
The Main Objectives Of SEO in Digital Marketing
How Artificial Intelligence Is Transforming Digital Marketing
Google CEO Sundar Pichai: Search will profoundly change in 2025
3 Most Important Business Growth Strategies
Top 20 Work From Home Job Skills
SEO Tips and Strategies For Small Businesses
Google is making a major change to Local Service Ads